Voice recognition technology, also known as automatic speech recognition (ASR), is an advanced field within artificial intelligence and linguistics that allows machines to interpret and process human speech. It is a complex system involving several stages of processing to convert spoken language into text or commands that a machine can understand and act upon.
Text to Speech (TTS) technology is a powerful tool that converts written text into spoken words, enabling machines to communicate with users in a natural and accessible way. TTS systems are widely used in various applications, from assistive devices for the visually impaired to virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa. By synthesizing human-like speech from digital text, TTS bridges the gap between human and machine interaction, making information accessible to a broader audience. This technology has significantly improved over the years, delivering more natural and expressive speech outputs that enhance user experience.
How Voice Recognition Technology Works
Voice recognition systems work by capturing sound waves produced by a speaker, analyzing these waves, and then converting them into a digital format that can be processed by algorithms. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the stages involved:
1. Audio Signal Acquisition
The first step in voice recognition is capturing the audio signal. This is typically done using a microphone, which converts sound waves into an electrical signal. The quality of this signal is critical, as noisy or unclear input can reduce the accuracy of the recognition system.
2. Pre-processing of the Signal
Once the audio signal is captured, it undergoes several pre-processing steps to enhance its quality and extract the relevant features. These steps include:
- Noise Reduction: Background noise is filtered out to improve clarity.
- Normalizing Volume Levels: The signal’s amplitude is adjusted to ensure consistent input levels.
- Segmentation: The continuous stream of audio is divided into smaller, manageable segments called frames, typically 10 to 25 milliseconds long.
3. Feature Extraction
Feature extraction is the process of analyzing the audio segments to identify characteristics that can be used to differentiate one sound or word from another. The most common techniques used for feature extraction include:
- Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC): This technique transforms the audio signals into a spectrum that emphasizes the frequencies most relevant to human speech.
- Linear Predictive Coding (LPC): LPC analyzes the signal and predicts the next sample in the sequence, reducing the amount of data that needs to be processed while preserving the essential information.
4. Acoustic Modeling
Acoustic models are mathematical representations of the different sounds (phonemes) in a language. These models use statistical methods, such as Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) or deep learning techniques, to predict the probability of a particular sound occurring given a specific segment of the input signal.
- Hidden Markov Models (HMMs): HMMs are statistical models that represent the probabilities of sequences of observed events, such as the likelihood of certain phonemes following others.
- Deep Neural Networks (DNNs): DNNs, especially Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), are increasingly used for acoustic modeling due to their ability to model complex patterns in data.
5. Language Modeling
Language models predict the likelihood of a sequence of words. These models use the context provided by previous words to improve the accuracy of the transcription. There are two primary types of language models:
- N-gram Models: These models predict the probability of a word based on the preceding ‘n-1’ words.
- Neural Language Models: These models use deep learning architectures like Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks to capture more complex language patterns and dependencies.
6. Decoding
The decoding process involves combining the acoustic and language models to interpret the audio signal. This is done by searching for the sequence of words that has the highest probability given the acoustic input and the language model. The Viterbi algorithm, a dynamic programming algorithm, is commonly used for this purpose.
7. Post-processing
Once the decoding process is complete, post-processing steps are taken to refine the output. This may include correcting grammatical errors, handling punctuation, and managing homophones (words that sound the same but have different meanings).
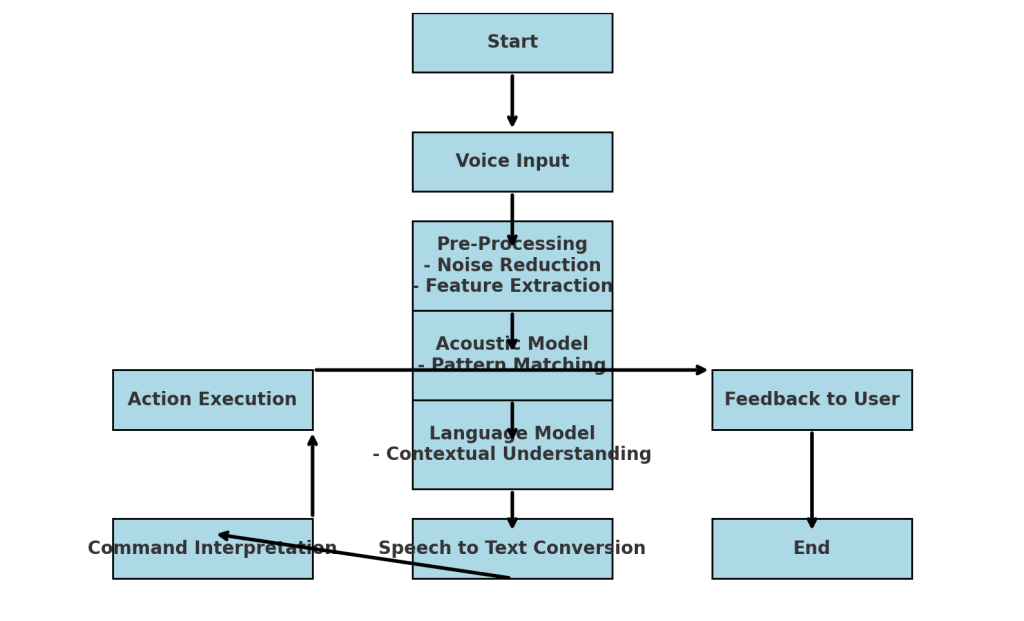
Diagram of Voice Recognition Process
Creating a diagram for voice recognition technology involves illustrating the flow from the input of the audio signal to the final text output. Below is a step-by-step guide that a diagram might follow:
Microphone
↓
Audio Signal
↓
Pre-processing (Noise Reduction, Segmentation)
↓
Feature Extraction (MFCC, LPC)
↓
Acoustic Model (HMMs, DNNs)
↓
Language Model (N-gram, LSTM)
↓
Decoding (Viterbi Algorithm)
↓
Text Output
This diagram represents the sequential processing stages in a simplified manner.
Technical Challenges in Voice Recognition
While voice recognition technology has advanced significantly, several challenges remain:
- Accents and Dialects: Variations in pronunciation can affect the system’s accuracy.
- Background Noise: Even with advanced noise reduction techniques, a noisy environment can still degrade performance.
- Homophones and Context: Understanding the correct meaning of words that sound the same but have different meanings requires advanced contextual analysis.
- Real-time Processing: Providing accurate results in real-time remains a computational challenge, especially for mobile and embedded devices.
Statistical Performance of Voice Recognition Systems
As per recent studies, modern voice recognition systems can achieve word error rates (WER) as low as 5% under ideal conditions. However, in noisy environments or with strong accents, WER can rise significantly. For instance, as per a 2021 study, the average WER for leading systems like Google’s ASR was approximately 8% in challenging environments.
Conclusion
Voice recognition technology is a sophisticated blend of signal processing, statistical modeling, and machine learning. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect improvements in accuracy, real-time processing capabilities, and the ability to handle diverse languages and dialects. Understanding the underlying mechanics helps in appreciating the complexities and innovations driving this technology forward.
For more technical insights, you can explore detailed academic papers and resources available on platforms like IEEE Xplore and Google Scholar.





 How to Choose the Right Digital Agency for Outsourcing Your Digital PR?
How to Choose the Right Digital Agency for Outsourcing Your Digital PR?